Epididymitis Orchitis
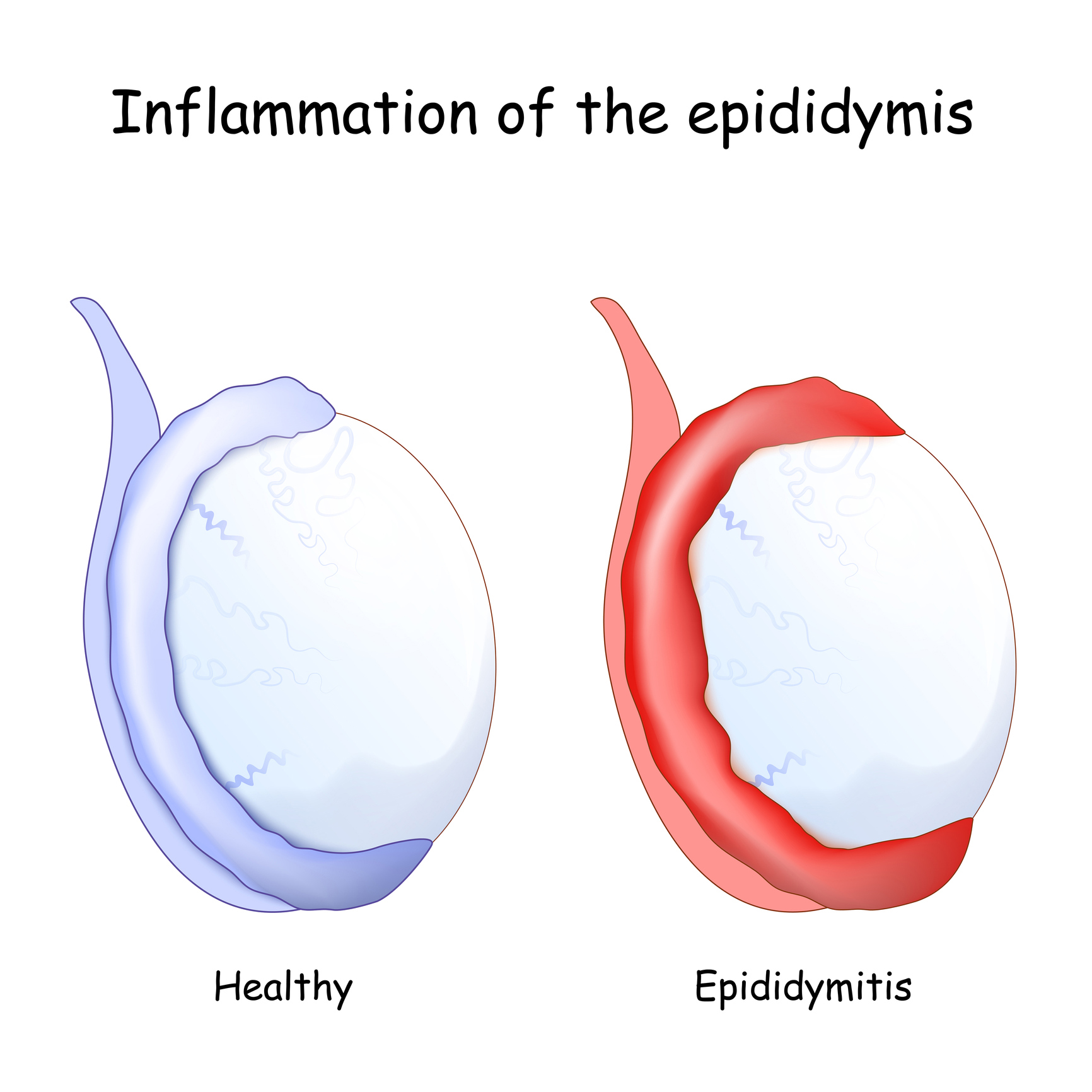
Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis, a tube at the back of the testicles that stores and carries sperm. The condition commonly affects men aged 14-35 years. Epididymitis is often caused by bacterial infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
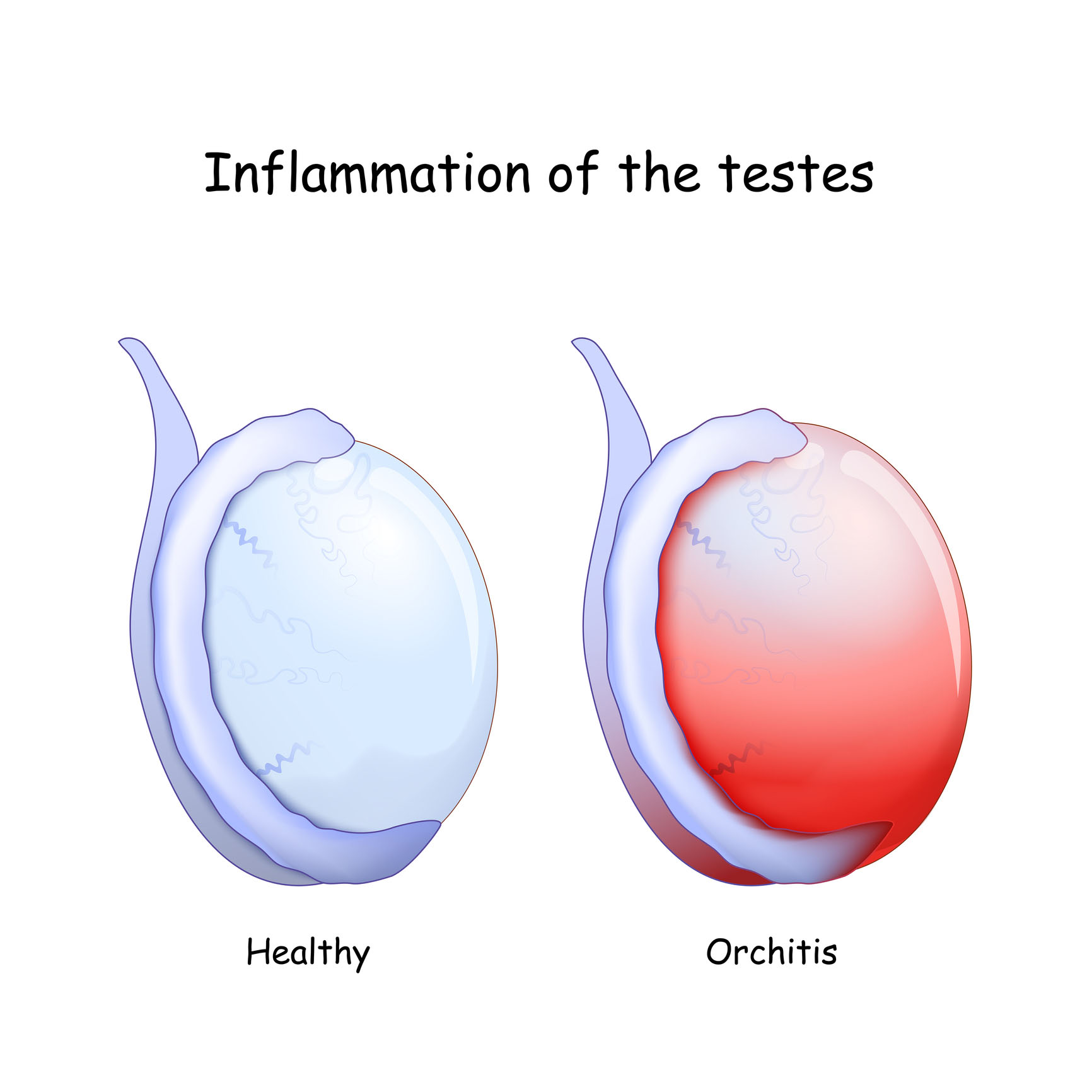
Orchitis is the inflammation of one or both testicles. It is caused by bacterial or viral infections, again, mostly the result of STIs. In some cases, the mumps virus can cause orchitis.
Bacterial orchitis might be associated with epididymitis. When that happens, it is called epididymo-orchitis. In this condition, the patient experiences sudden swelling of both the epididymis and the testis.
Epididymitis & Orchitis Symptoms
Symptoms of epididymitis and orchitis include a red and swollen scrotum, testicle pain and tenderness, painful urination, frequency in urination, penile discharge, blood in semen, and pain or discomfort in the pelvic area. For orchitis, fever, nausea and vomiting may develop as well.
Causes of Epididymitis & Orchitis
Causes of epididymitis and orchitis include:
- STIs, such as gonorrhoea and chlamydia
- History of prostate or urinary tract infections (UTI)
- History of medical procedures that affect the urinary tract, such as insertion of a urinary catheter or scope into the penis
- An uncircumcised penis or an anatomical abnormality of the urinary tract
- Prostate enlargement
- Viral infections, such as the mumps virus
- Trauma, such as a groin injury
Epididymitis & Orchitis Diagnosis
The following procedures can help your urologist diagnose epididymitis or orchitis:
- Physical examination to check for enlarged lymph nodes in the groin or an enlarged testicle
- Rectal examination to check for prostate enlargement or tenderness
- STI screening
- Urine and blood tests to analyse for abnormalities
- Ultrasound of the testicle
Epididymitis & Orchitis Treatment Options
Treatments for epididymitis and orchitis are usually antibiotics medication. Resting, supporting the scrotum with an athletic supporter, applying ice packs, and taking pain medication can help relieve discomfort. Your urologist will check if the infection has cleared in your follow-up visit. Surgery will be considered if epididymitis or orchitis is due to underlying physical abnormalities.
Why should you choose Dr Colin Teo to perform Epididymitis / Orchitis treatment?
Dr Colin Teo is the Founding Head of Khoo Teck Puat Hospital’s Urology Department, with years of experience in minimally invasive keyhole surgery, operating with precision surgical techniques. Many fellows have trained under his mentorship. He did a Fellowship in EndoLaparoscopy and Andrology at St James’ Hospital in Leeds, UK and was sponsored for a Senior Healthcare Medical Development Program (HMDP) in Advanced Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery at University of Southern California (USC) Keck Hospital in Los Angeles, USA. Dr Teo is also the President of the Society for Men’s Health.
Seek recommendations on suitable treatment options for epididymitis and orchitis with Colin Teo Urology. Contact us to book an appointment today.