Prostatitis
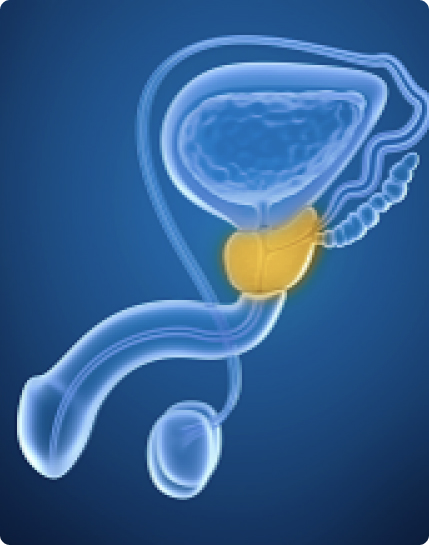
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland in between the bladder and the urethra that nourishes and transports sperm. The prostate can sometimes be enlarged because of inflammation. Inflammation of the prostate is known as prostatitis, and this can cause swelling and pain.
Prostatitis Symptoms
There are several types of prostatitis, each with a range of symptoms.
- Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is the most common prostate inflammation. Symptoms include pain and difficulties during urination, persistent pain in the bladder, testicles or between the penis and the rectal region, or pain during ejaculation.
-
There are two types of prostatitis associated with bacterial infection. In chronic bacterial prostatitis, the feeling of discomfort come and go as it is a long-term condition. You may feel a burning sensation during urination, a frequent urge to urinate, pain during ejaculation, or persistent pain in the bladder, testicles or between the penis and the rectal region.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is usually sudden and painful. You may experience sudden chills, fever, or a painful burning sensation during urination. You may also have difficulties emptying your bladder. - The last type of prostatitis is asymptomatic prostatitis, and it does not cause any discomfort. This is usually detected during an examination for other conditions, and treatment is often not required.
CAUSES of Prostatitis
Some cases of prostatitis are clearly related to acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis infections. These infections get into the prostate from the urethra by the backward flow of infected urine into the prostate ducts. Bacterial prostatitis is not contagious and is not a sexually transmitted disease.
Some of the causes of prostatitis can include:
- Recent medical procedure where a medical instrument, such as a urinary catheter, is inserted
- Rectal intercourse engagement
- Abnormal urinary tract
- Recent bladder infection
- Enlarged prostate
- Autoimmune disease (an abnormal reaction of the body to the prostate tissue)

The prostate is a walnut-sized gland in between the bladder and the urethra that nourishes and transports sperm. The prostate can sometimes be enlarged because of inflammation. Inflammation of the prostate is known as prostatitis, and this can cause swelling and pain.
Prostatitis Symptoms
There are several types of prostatitis, each with a range of symptoms.
- Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is the most common prostate inflammation. Symptoms include pain and difficulties during urination, persistent pain in the bladder, testicles or between the penis and the rectal region, or pain during ejaculation.
-
There are two types of prostatitis associated with bacterial infection. In chronic bacterial prostatitis, the feeling of discomfort come and go as it is a long-term condition. You may feel a burning sensation during urination, a frequent urge to urinate, pain during ejaculation, or persistent pain in the bladder, testicles or between the penis and the rectal region.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is usually sudden and painful. You may experience sudden chills, fever, or a painful burning sensation during urination. You may also have difficulties emptying your bladder. - The last type of prostatitis is asymptomatic prostatitis, and it does not cause any discomfort. This is usually detected during an examination for other conditions, and treatment is often not required.

Causes of Prostatitis
Some cases of prostatitis are clearly related to acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis infections. These infections get into the prostate from the urethra by the backward flow of infected urine into the prostate ducts. Bacterial prostatitis is not contagious and is not a sexually transmitted disease.
Some of the causes of prostatitis can include:
- Recent medical procedure where a medical instrument, such as a urinary catheter, is inserted
- Rectal intercourse engagement
- Abnormal urinary tract
- Recent bladder infection
- Enlarged prostate
- Autoimmune disease (an abnormal reaction of the body to the prostate tissue)
Prostatitis Diagnosis
If symptoms of prostatitis are present, a physical exam and a digital rectal exam (DRE) will be performed to determine the severity. The following additional tests may be ordered to confirm a diagnosis:
- CBC (complete blood count)
- Urine tests to check for bacteria
- Blood chemistry tests
- PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) test
Prostatitis Treatment Options
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of prostatitis. Prostatitis treatment is usually done through medications. Antibiotics may be given if the cause of your prostate inflammation is bacterial. Other medications include alpha-blockers that help to relax the prostate and bladder area or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that help to relieve pain and swelling.
If further intervention is required, low-intensity shockwave therapy (LiSWT) procedure may be performed. Low energy shockwaves are sent to the prostate to help improve blood flow, relieve pain, and reduce inflammation.
Supportive therapies for chronic prostatitis include stool softeners and prostate massage.
Seek recommendations on suitable treatment options for Prostatitis with Colin Teo Urology. Contact us to book an appointment today.