Urinary Stones
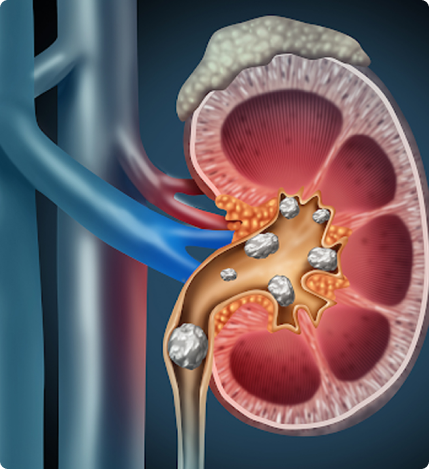
Urinary Stones
Stone disease occurs when chemicals in your urine become concentrated and form crystals in your urinary tract. It can affect your kidneys, bladder, the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder (ureters), or the tube that connects your bladder to the outside of your body (urethra).
Men are more likely to develop them than women. Other factors such as dehydration, obesity, and a family history of stone disease can also increase your risk.
Urinary Stones Symptoms
When these stones get stuck in any part of your urinary tract, they can cause bleeding or infection. Depending on their location, they may block the flow of urine, causing colic or intermittent pain. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, blood in urine, fever, and painful urination. Patients with urinary stones either report pain or the stones are picked up incidentally during health screening scans.
Urinary Stones diagnosis
Imaging is often used to diagnose urinary stones. Some types of imaging that we may suggest include:
- Abdominal and pelvic CT: This is the most rapid scanning method for locating a stone. This procedure can provide detailed images of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, identify a stone, and reveal whether it is blocking urinary flow.
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP): This is an x-ray examination of the kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder that uses iodinated contrast material injected into veins to evaluate the urinary system.
- Abdominal and Pelvic ultrasound: These exams use sound waves to provide pictures of the kidneys and bladder. They can identify blockage of urinary flow and help identify stones.


Urinary Stones
Stone disease occurs when chemicals in your urine become concentrated and form crystals in your urinary tract. It can affect your kidneys, bladder, the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder (ureters), or the tube that connects your bladder to the outside of your body (urethra).
Men are more likely to develop them than women. Other factors such as dehydration, obesity, and a family history of stone disease can also increase your risk.
Urinary Stones Symptoms
When these stones get stuck in any part of your urinary tract, they can cause bleeding or infection. Depending on their location, they may block the flow of urine, causing colic or intermittent pain. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, blood in urine, fever, and painful urination. Patients with urinary stones either report pain or the stones are picked up incidentally during health screening scans.

Urinary Stones diagnosis
Imaging is often used to diagnose urinary stones. Some types of imaging that we may suggest include:
- Abdominal and pelvic CT: This is the most rapid scanning method for locating a stone. This procedure can provide detailed images of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, identify a stone, and reveal whether it is blocking urinary flow.
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP): This is an x-ray examination of the kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder that uses iodinated contrast material injected into veins to evaluate the urinary system.
- Abdominal and Pelvic ultrasound: These exams use sound waves to provide pictures of the kidneys and bladder. They can identify blockage of urinary flow and help identify stones.
Urinary Stones Treatment Options
Treatment will depend on the type, size, and location of the stone, including the patient’s symptoms. Most kidney stones will not require invasive treatment. They may be passed out by drinking water alone and using pain medications. For large stones causing symptoms, more invasive procedures may have to be performed.
- Ureteroscopy & Laser Lithotripsy (URS & LL): A thin lighted scope known as the ureteroscope is inserted through your urethra and bladder to your ureter. Once the stone is located, a laser beam will break it into pieces that will then be passed in your urine. A stent is inserted in the ureter to relieve swelling and help healing. This is the most common endoscopic procedure performed to treat kidney stones, providing patients with quick relief of symptoms.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): ESWL uses sound waves to create strong vibrations (shock waves) that break the stones into smaller fragments that can be passed in your urine. Depending on the type and size of stone, this treatment may not be suitable. We will assess the patient before recommending the best treatment to ensure a better stone clearance rate.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): PCNL involves surgically removing a kidney stone using small instruments inserted through a small cut in your back. This procedure is used for larger kidney stones.
- Tubeless removal of large stones: This is similar to the percutaneous stone treatment, but you will be given an internal stent for draining urine instead of an external tube, which reduces pain, the length of time you will spend in the hospital, and post-operative wound care.
You will have anaesthesia or sedation for these procedures, so you will not feel any pain. You may also need to make lifestyle changes post-treatment to help prevent the recurrence of urinary stones, such as by eating lots of fruits and vegetables and drinking plenty of fluids.