Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system. A UTI is the abnormal growth of bacteria associated with abnormal symptoms. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract—the bladder and the urethra.
Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than men. Serious consequences can occur if a UTI is not treated or spreads to your kidneys.
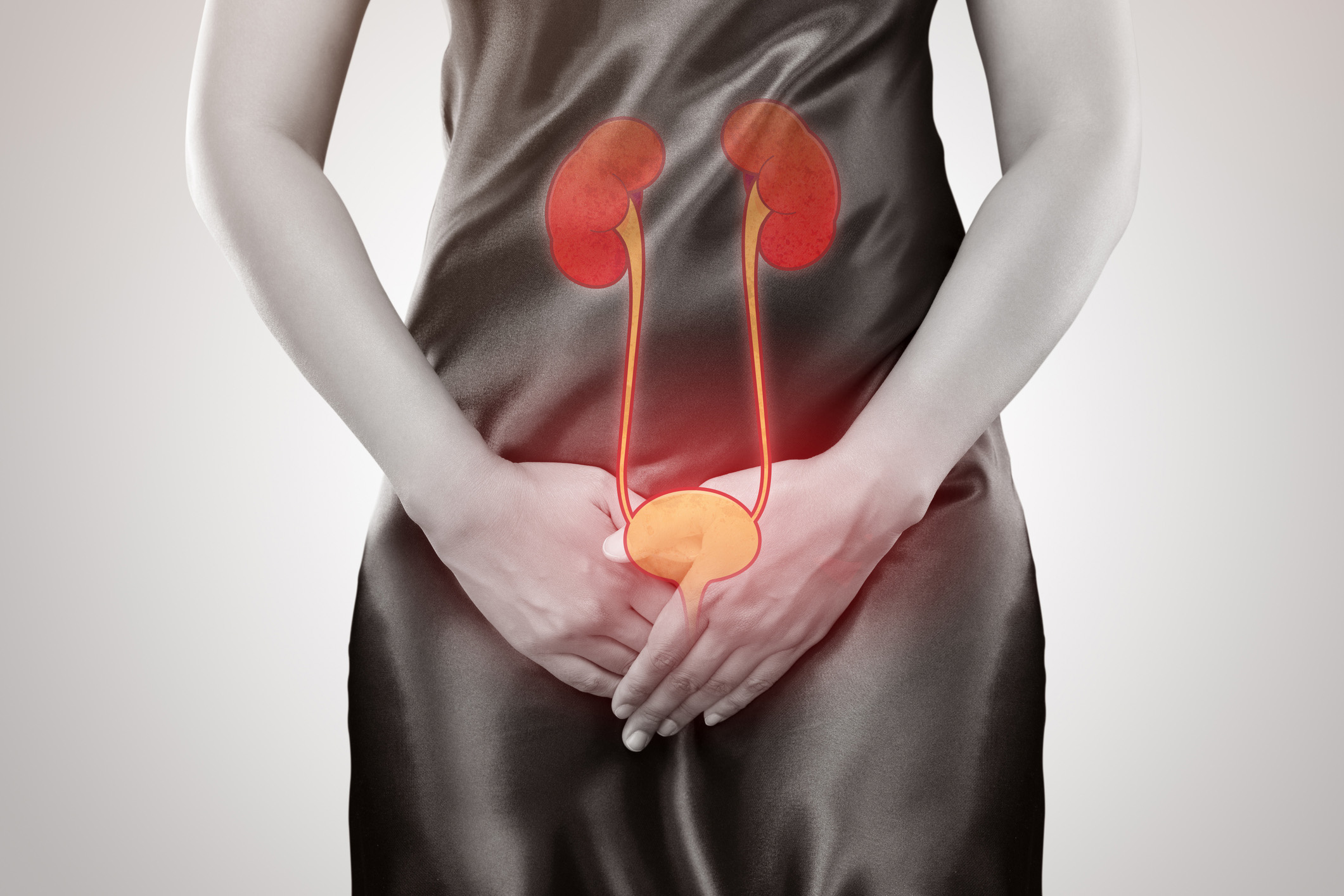
Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
Consult your urologist if you are experiencing these symptoms:
- Strong, persistent urge to urinate
- Burning when urination
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy or reddish, a sign of blood in the urine
- Strong-smelling urine
- In women, an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
- In men, a sensation of fullness in the rectum
- If the infection has reached the kidneys, other symptoms include fever, pain in the back or side below the ribs, nausea or vomiting
Causes of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enters the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. This happens more often in women because a woman's urethra opening is closer to the anus than in men.
Risks factors include sexual activity, certain types of birth control, urinary tract blockages, kidney stones, catheter use, and menopause.
Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis
Your urologist will perform an examination focused on the abdomen and genitalia and possibly a digital rectal exam (for male patients).
Additional tests may include urinalysis (to check for any blood in the urine or infection), post-void residual, renal/bladder ultrasound, and cystoscopy.
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment Options
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. There are many different types of antibiotics to treat infections, depending on the bacteria you have. If the infection is simple and there is no obstruction, a UTI can be cured within 1-2 days of treatment. However, it is important to still finish your course of antibiotics (for at least a week).
Postmenopausal women with UTIs may be helped by topical (vaginal) hormone replacement with estrogen.
If you have a kidney infection, you will be on a longer course of antibiotics, and the antibiotic therapy may be started intravenously (IV) in the hospital.
Only in cases of anatomical abnormalities, kidney stones, or foreign bodies, surgery may be necessary.
Seek recommendations on suitable treatment options for Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) with Colin Teo Urology. Contact us to book an appointment today.